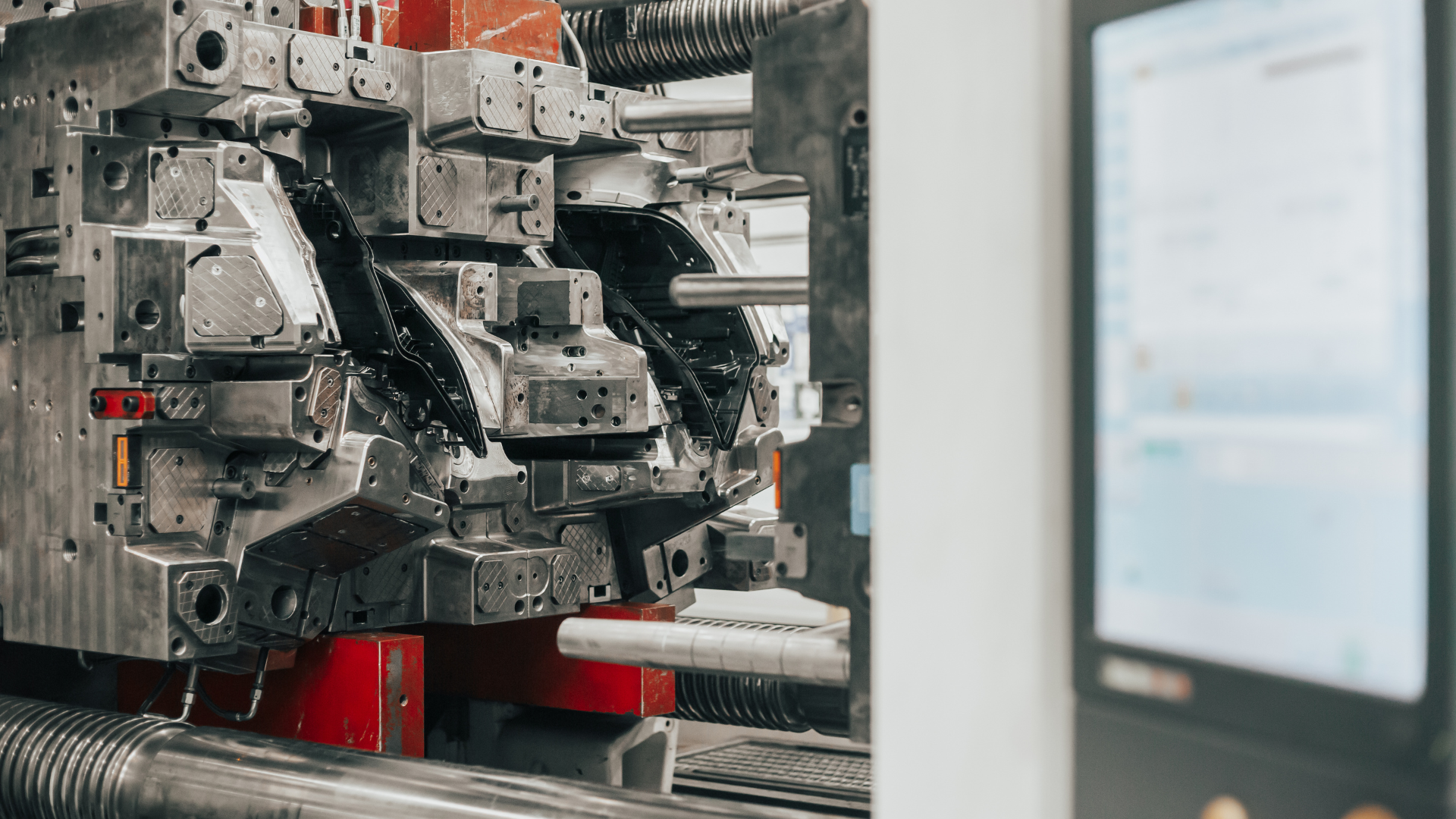
In the fast-paced world of manufacturing, staying ahead of the competition requires not only innovative ideas but also efficient production processes.
One such method that has revolutionized the way products are brought to market is injection molding. This versatile manufacturing technique has become a cornerstone for businesses aiming to meet consumer demands promptly.
1. The Basics of Injection Molding:
Before we explore its impact on production efficiency, it’s crucial to understand the fundamentals of injection molding.
At its core, injection molding is a manufacturing process where molten material is injected into a mold, solidifying it into the desired shape. This technique is commonly used for the mass production of identical items, making it ideal for industries ranging from automotive to consumer goods.
2. Speeding Up Production:
One of the key advantages of injection molding is its ability to accelerate the production timeline significantly. Traditional manufacturing methods often involve multiple steps, such a cutting, shaping, and assembling, which can be time-consuming.
Injection molding, however, streamlines these processes into a single step, reducing production time and cost.
2a. Rapid Prototyping:
Injection molding allows for the creation of prototypes quickly and economically. This enables businesses to iterate and refine their product designs efficiently, ensuring that the final product meets both quality standards and consumer expectations.
Rapid prototyping not only expedites the development phase but also minimizes the risk of errors and design flaws.
2b. High Production Speeds:
Once the final design is approved, injection molding can produce large quantities of identical products at an impressive speed. The automated nature of the process ensure consistent quality and precision, making it an ideal solution for businesses aiming to meet tight production schedules.
3. Cost-effective Mass Production:
Injection molding proves to be a cost-effective solution for mass production due to its efficient and ability to produce large quantities in a single cycle.
The automation of the process reduces labor costs, and the use of molds ensure minimal material waste. As a result, businesses can achieve economies of scale, making each unit more cost-effective to produce.
4. Material Selection and Versatility:
Another factor contributing to the efficient of injection molding is the wide range of materials available to use. From plastics and metals to ceramics, the versatility of injection molding allows businesses to choose materials that best suit their product requirements.
This adaptability not only enhances functionality of the final product but also streamlines the manufacturing process by catering to diverse industry needs.
| Material | Description | Ideal for | Finishes |
| ABS | Thermoplastic material that is known for its high impact strength, toughness, and affordability | Automotive trim, housings, and consumer goods | Polishing, texturing, or painting |
| Acrylic | Transparent thermoplastic material that is known for its optical clarity, UV resistance, and scratch resistance | Lighting fixtures, displays, and lenses | Polishing, texturing, or painting |
| Elastomer/rubber | Flexible and elastic material that is used to create parts such as seals, gaskets, and other components that require flexibility and compression | Seals, gaskets, and other components that require flexibility and compression, such as in automotive, medical, and consumer goods applications | Painting or powder coating |
| Glass-filled PC, ABS, Nylon | Reinforced thermoplastic materials that are made by blending glass fibers with the base material, increasing their strength, stiffness, and heat resistance | Automotive and aerospace components, electronic housings, and industrial equipment | Painting or powder coating |
| Nylon | Versatile engineering thermoplastic material that is known for its high strength, toughness, and durability | Gears, bearings, and structural components in automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications | Painting or powder coating |
| PC | High-performance engineering thermoplastic material that is known for its excellent impact strength, heat resistance, and transparency | Automotive and aerospace components, electronic housings, and medical equipment | Polishing, texturing, or painting |
| PC+ABS | Blend of PC and ABS materials that combines the toughness of ABS with the heat resistance of PC | Automotive interiors, electronic housings, and appliances | Polishing, texturing, or painting |
| TPO | Thermoplastic material that is known for its excellent impact strength, weather resistance, and affordability | Automotive components such a s bumpers, fenders, and door panels | Polishing, texturing, or painting |
| ULTEM 1000 | High-performance engineering thermoplastic material that is known for its excellent heat resistance, strength, and stiffness | High-performance parts such as aerospace components, electrical insulators, and medical equipment | Polishing, texturing, or post-processed with coatings to improve their resistance to heat and chemical exposure |
| ULTEM 2300 | High-performance engineering thermoplastic material that is known for its excellent heat resistance, strength, and stiffness, with added flame-retardant properties | High-performance parts such as electrical components and structural parts in aircrafts and trains | Polishing, texturing, or post-processed with coatings to improve their resistance to heat and chemical exposure |
5. Meeting Consumer Demands:
In today’s consumer-driven market, the ability to respond quickly to changing trends and demands is paramount. Injection molding empowers businesses to do just that by providing a rapid and cost-effective means of production.
The shorter production cycles and efficient prototyping enable manufacturers to keep pace with consumer preferences and bring products to market swiftly.
6. Environmental Considerations:
While the focus has primarily been on speed and efficiency, it’s important to note that injection molding also aligns with environmentally friendly practices. The reduction in material waste, energy-efficient processes, and the recyclability of many materials used in injection molding contribute to a more sustainable approach to manufacturing.
Injection molding plays a pivotal role in fast-tracking the production processes for businesses across various industries. From rapid prototyping to cost-effective mass production, the advantages of injection molding are evident in its contribution to efficient and responsiveness.
A consumer demands continue to evolve, the adaptability and speed offered by injection molding position it as a cornerstone in the journey from concept to market, enabling businesses to thrive in an ever-changing landscape.